CAUSES OF DEATH
UNDERLYING AND CONTRIBUTING FACTORS
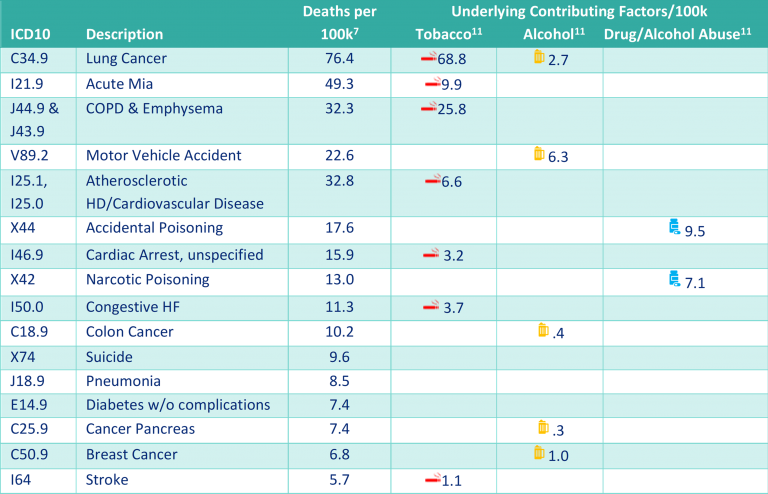
When evaluating the cause of death, it is essential to examine and understand the underlying and contributing factors that result in the diagnoses of specific diseases and causes of death. While genetics and environmental factors have a part, behavior plays a much larger role in developing particular diseases that result in death than was believed in the past.
In 2009-2010, at least 47% of adults in the U.S. had at least one risk factor for heart disease8. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), three prevailing risk factors contribute to the incidence of heart disease including uncontrolled high blood pressure, uncontrolled high low-density lipoproteins cholesterol (LDL), and smoking. (The first two of which can be exacerbated by behavior and the last being solely a behavior.) Similarly, 90% of all lung cancers are the result of smoking tobacco9 and 80% of all patients diagnosed with COPD are or were smokers10.
An examination of the underlying causes of premature death (death before age 75)7, for Gallatin County residents, shows behavioral factors significantly affect lower life expectancy trends compared with the nation and state overall. Those behaviors include smoking, alcohol use, and drug/alcohol abuse11.